Linux file permissions
File Permission
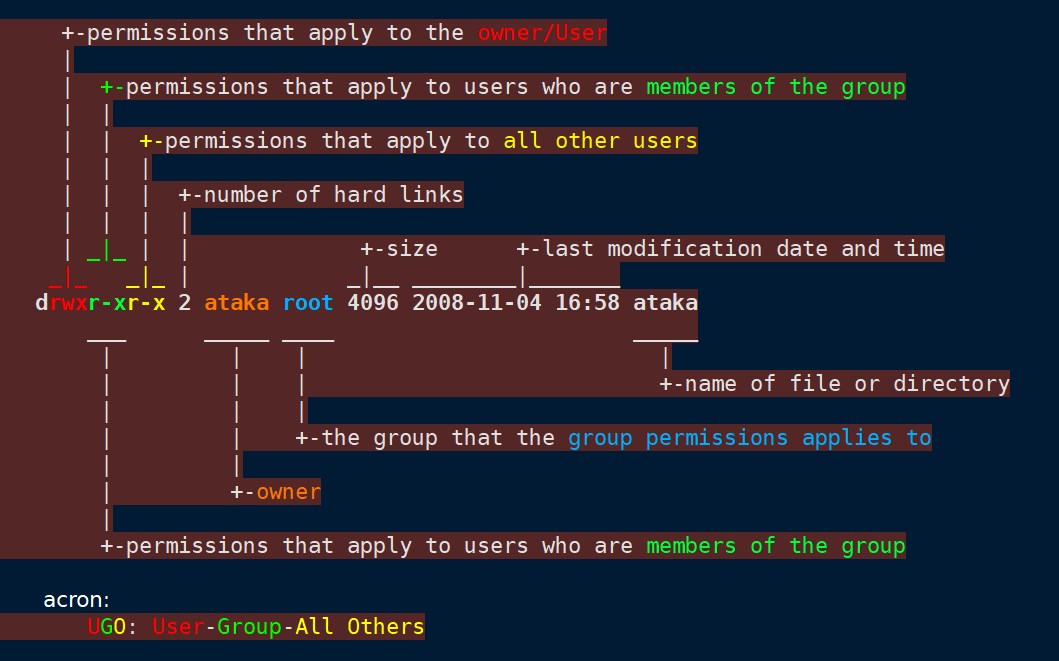
Command: ls -la
4 = Read
2 = Write
1 = Execute
0 = No Permission
Permission numbers are:
0 = ---
1 = --x
2 = -w-
3 = -wx
4 = r-
5 = r-x
6 = rw-
7 = rwx
stat - file permissions with number format
stat -c '%A %a %U %G %n' burpsuite.jar
Output: -rw-r--r-- 644 root root burpsuite.jar
%Afile permissions
%afile permissions in number format
%Ufile owner
%Gfile group
%nfile name
chmod
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
chmod g+w filename | add w (write) to group. |
chmod g-wx filename | remove wr (write,read) to group. |
chmod o+w filename | add w to others. |
chmod o-rwx foldername | remove rwx to others. |
chmod ugo+rwx foldername | to give read, write, and execute to everyone. |
chmod a=r foldername | to give only read permission for everyone. |
chown
chown [OPTION]... [OWNER][:[GROUP]] FILE...
chown [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...
These commands will give ownership to someone, but all sub files and directories still belong to the original owner.
-
chown name filename -
chown name foldername-Rrecursive You can also combine the group and ownership command by using:chown -R owner:group /home/name/directoryname
chgrp
chgrp [OPTION]... GROUP FILE...
chgrp [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...
chgrp groupname filenamechgrp groupname foldername
Ref
Derek Rook - file permissions:
Linux file Permissions
Mastering Linux Permissions